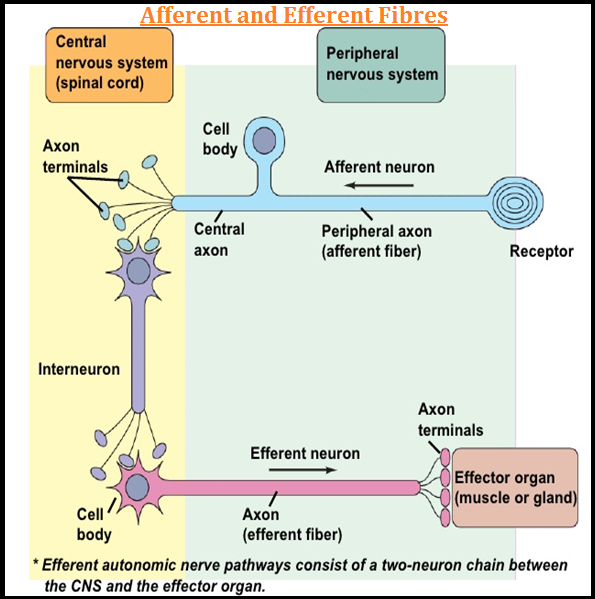
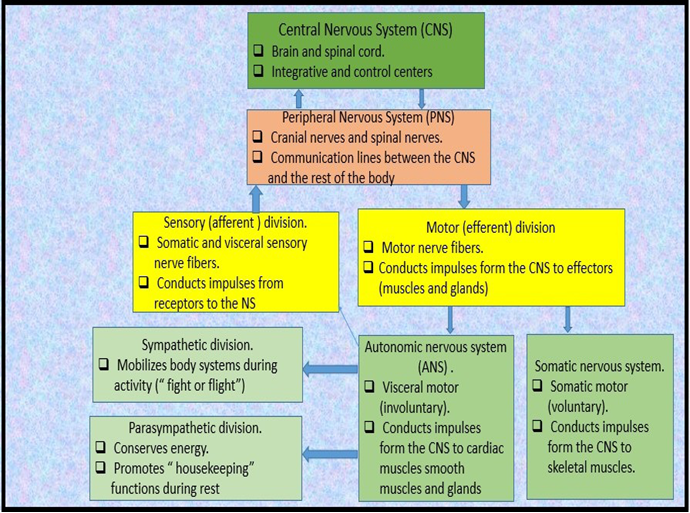
● A `color{violet}("Neuron")` is the `color{brown}("structural and functional unit")` of `color{violet}("neural system.")`
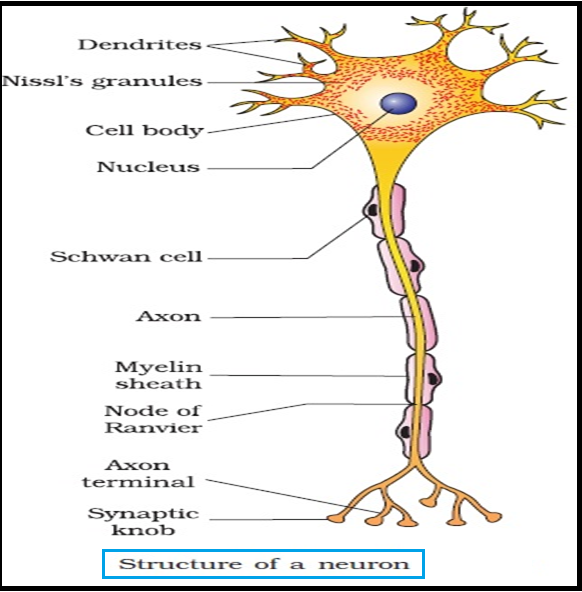
● A `color{violet}("neuron")` is a `color{violet}("microscopic structure")` composed of three major parts, namely, `color{violet}("cell body")`, `color{violet}("dendrites and axon.")`
● The `color{violet}("cell body")` contains cytoplasm with typical `color{violet}("cell organelles")` and certain granular bodies called `color{brown}("Nissl’s granules.")`
● Short `color{violet}("fibres")` which branch repeatedly and project out of the `color{violet}("cell body ")` also contain `color{violet}("Nissl’s granules")` and are called `color{brown}("dendrites.")`
● These `color{violet}("fibres transmit impulses")` towards the `color{violet}("cell body.")`
● The `color{brown}("axon")` is a `color{violet}("long fibre")`, the `color{violet}("distal end")` of which is branched.
● Each branch terminates as a `color{violet}("bulb-like structure")` called `color{brown}("synaptic knob")` which possess `color{violet}("synaptic vesicles")` containing chemicals called `color{brown}("neurotransmitters.")`
● The `color{violet}("axons transmit")` nerve impulses away from the `color{violet}("cell body")` to a `color{brown}("synapse")` or to a `color{brown}("neuro-muscular junction.")`
● Based on the number of `color{violet}("axon and dendrites,")` the `color{violet}("neurons")` are divided into three types, i.e.,
`star` `color{brown}("Multipolar")` (with one axon and two or more dendrites; found in the `color{brown}("cerebral cortex")`)
`star` `color{brown}("Bipolar")` (with one axon and one dendrite, found in the `color{brown}("retina of eye")`)
`star` `color{brown}("Unipolar")` (cell body with one axon only; found usually in the `color{brown}("embryonic stage")` ).
● There are two types of `color{violet}("axons,")` namely, `color{brown}("myelinated")` and `color{brown}("nonmyelinated.")`
● The `color{violet}("myelinated")` nerve `color{violet}("fibres")` are enveloped with `color{brown}("Schwann cells,")` which form a `color{violet}("myelin sheath")` around the axon.
● The `color{violet}("gaps between")` two adjacent `color{violet}("myelin sheaths")` are called `color{brown}("nodes of Ranvier.")`
● `color{violet}("Myelinated nerve fibres")` are found in `color{brown}("spinal and cranial nerves.")`
● Unmyelinated nerve fibre is enclosed by a `color{violet}("Schwann cell")` that does not form a `color{violet}("myelin sheath")` around the axon, and is commonly found in `color{brown}("autonomous")` and the `color{brown}("somatic neural systems.")`
● A `color{violet}("Neuron")` is the `color{brown}("structural and functional unit")` of `color{violet}("neural system.")`
● A `color{violet}("neuron")` is a `color{violet}("microscopic structure")` composed of three major parts, namely, `color{violet}("cell body")`, `color{violet}("dendrites and axon.")`
● The `color{violet}("cell body")` contains cytoplasm with typical `color{violet}("cell organelles")` and certain granular bodies called `color{brown}("Nissl’s granules.")`
● Short `color{violet}("fibres")` which branch repeatedly and project out of the `color{violet}("cell body ")` also contain `color{violet}("Nissl’s granules")` and are called `color{brown}("dendrites.")`
● These `color{violet}("fibres transmit impulses")` towards the `color{violet}("cell body.")`
● The `color{brown}("axon")` is a `color{violet}("long fibre")`, the `color{violet}("distal end")` of which is branched.
● Each branch terminates as a `color{violet}("bulb-like structure")` called `color{brown}("synaptic knob")` which possess `color{violet}("synaptic vesicles")` containing chemicals called `color{brown}("neurotransmitters.")`
● The `color{violet}("axons transmit")` nerve impulses away from the `color{violet}("cell body")` to a `color{brown}("synapse")` or to a `color{brown}("neuro-muscular junction.")`
● Based on the number of `color{violet}("axon and dendrites,")` the `color{violet}("neurons")` are divided into three types, i.e.,
`star` `color{brown}("Multipolar")` (with one axon and two or more dendrites; found in the `color{brown}("cerebral cortex")`)
`star` `color{brown}("Bipolar")` (with one axon and one dendrite, found in the `color{brown}("retina of eye")`)
`star` `color{brown}("Unipolar")` (cell body with one axon only; found usually in the `color{brown}("embryonic stage")` ).
● There are two types of `color{violet}("axons,")` namely, `color{brown}("myelinated")` and `color{brown}("nonmyelinated.")`
● The `color{violet}("myelinated")` nerve `color{violet}("fibres")` are enveloped with `color{brown}("Schwann cells,")` which form a `color{violet}("myelin sheath")` around the axon.
● The `color{violet}("gaps between")` two adjacent `color{violet}("myelin sheaths")` are called `color{brown}("nodes of Ranvier.")`
● `color{violet}("Myelinated nerve fibres")` are found in `color{brown}("spinal and cranial nerves.")`
● Unmyelinated nerve fibre is enclosed by a `color{violet}("Schwann cell")` that does not form a `color{violet}("myelin sheath")` around the axon, and is commonly found in `color{brown}("autonomous")` and the `color{brown}("somatic neural systems.")`